2nd century Pax Romana, Paper and Buddha statue
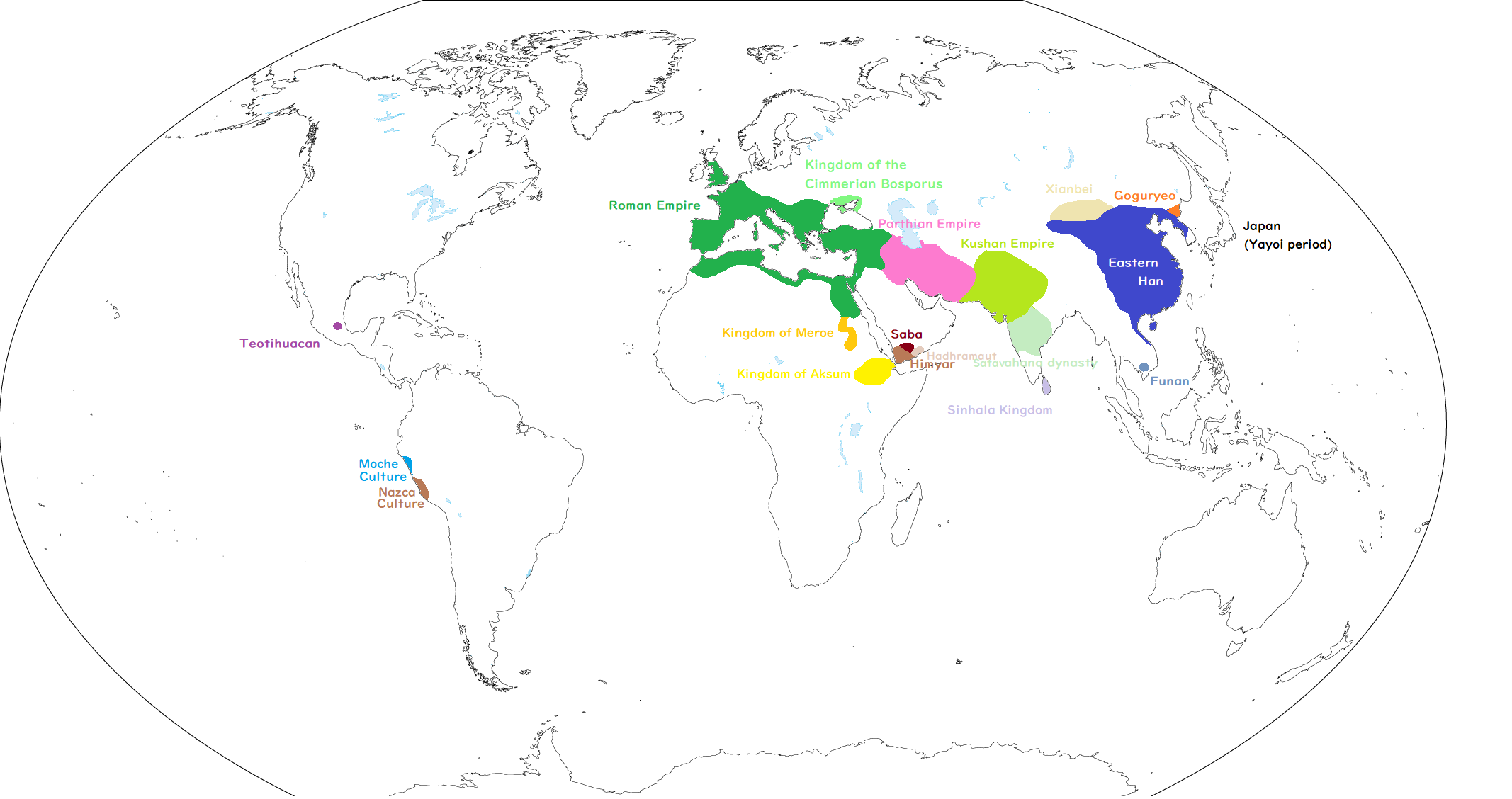
Romam Empire and the Han Dynasty flourished in the East and the West of Eurasia. Both countries continued to prosper well into the 2nd century, but by the end of the century they were entering a period of instability.
Europe
The era of the “Five Good Emperors”, which began with Nerva’s accession to the throne at the end of the 1st century, brought the empire to its peak. This was the period known as “Pax Romana” (Peace of Rome). Trajan, who succeeded Nerva, conquered the Dacian region (present-day Romania) and Armenia, achieving the greatest extent of the empire.
Hadrian, the third emperor, inspected the vast empire and made known the authority of the emperor, as well as introducing the culture and ideas of ancient Greece to Rome. Antoninus Pius, the fourth emperor, was a gentle man who maintained long-term peace without foreign wars.
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus, the fifth emperor, was also a philosopher and left behind excellent books such as “Meditations”. However, there followed a succession of less than excellent emperors, and as the regions that had been treated as Provinces began to develop economically, the absolute position of the city of Rome began to fluctuate.

In addition to the emperor, many scholars were active in the 2nd century. Plutarch wrote a series of “Parallel Lives” comparing the heroes of ancient Greece and Rome.
The physician Galen was also a man of this era, and he made great contributions to medicine by elucidating the structure of the body through dissection.
Middle East
On the other hand, the Jews living in what is now Israel continued to be subjected to pressure from the Roman Empire even after the revolt they had launched in the previous century, and they remained discontented with this oppression.
In 132 they once again rose up in a large-scale rebellion, but it too was suppressed, and they were even banned from entering and leaving Jerusalem. After this, the Jews sought a new promised land and dispersed to regions across the world, a movement known as the Diaspora.

※When Jewish Temple was destroyed was in 1st century.
The Parthian kingdom, located in what is present-day Iran and Iraq, continued to lose territory to the powerful Roman Empire, and gradually declined.
East Asia
At the beginning of the 2nd century in the Eastern Han(東漢) Dynasty, a revolutionary invention was created by the politician Cai Lun(蔡伦). This is the practical “paper.” After that, paper spread mainly in East Asia, and in the 8th century it also reached West Asia.
In China at this time, eunuchs (castrated bureaucrats. Cai Lun was also a eunuch) began to take charge of politics in place of the emperor, and the conflicts intensified with the maternal relatives and bureaucrats, who had been in power until then.
In 166, there was an incident in which people who criticized the eunuchs were persecuted, called “Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions”(黨錮之禍).
Farming villages were devastated by natural disasters, and people with anxiety began to believe in new religions. One of these religious groups started a large-scale peasant revolt called the “Yellow Turban Rebellion” (黄巾之乱, which shook the Later Han society. The central dynastic government, which had become useless, was replaced by local powerful people. One of them was Cao Cao (曹操).
On the Mongolian plateau, replacing the Xiongnu(匈奴) who had once troubled the Han Dynasty, another nomadic tribe called the Xianbei(鮮卑) became powerful. Xianbei society was unified by the competent leader Tanshihuai(檀石槐) and became a major force. Since then, it has repeatedly invaded Chinese society and had a major impact.
Trade between East and West , India
Under the Pax Romana, trade between East and West became more and more popular. In 166, there is a record that a person believed to be a messenger of Marcus Aurelius came to Vietnam, under Han rule at the time. This indicates that a trade route, the Silk Road, was being developed to connect the two countries.
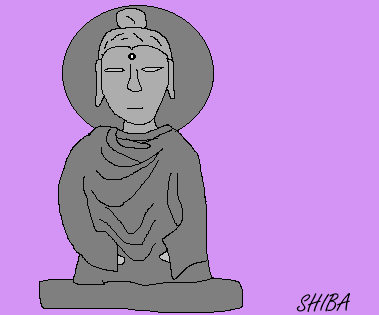
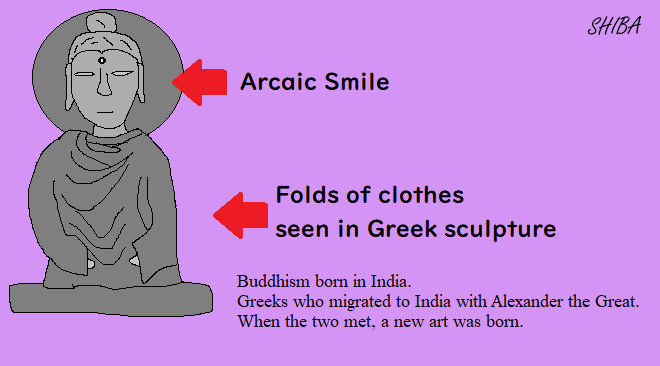
The Kushan dynasty, which ruled northern India, included the hub of Silk Road in its territory, and reached its peak during the reign of King Kanishka in the first half of the 2nd century. Kanishka protected Buddhism so well that the religion spread across a wide area from India to Central Asia. Particularly in the Gandhara region of northwestern India, Buddhist art including Buddhist statues flourished when stone statue art introduced from ancient Greece encountered Buddhism.
South East Asia
Besides the overland Silk Road that ran from India through Central Asia, a “Maritime Silk Road” also took shape, running across the Indian Ocean and through Southeast Asia.
As a result, port towns emerged even in Southeast Asia, which is covered with tropical rainforests, and some of them eventually developed into states. Funan(扶南), which arose in what is now Cambodia, and Linyi(林邑), which emerged in central and southern Vietnam, were representative examples of such polities.
Events
Early 2nd century Funan established in the southern part of the Indochina Peninsula. (Southeast Asia)
105 Cai Lun developed of paper manufacturing method. (China)
117 The area of the Roman Empire became the largest. (Rome)
122 Hadrian’s Wall built (Britain)
around 125 Saka advances into the Indus River basin (South Asia)
around 128 Kanishka ascended the throne in the Kushan dynasty (India/Central Asia)
135 Roman army suppressed Jewish rebellion and excluded them from Jerusalem. Jewish diaspora started. (Rome/West Asia)
156 Nomads Xianbei was unified under Tanshihuai. (East Asia)
166 Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions (China)
184 Yellow Turban Rebellion (China)
around 192 Champa Kingdom established in eastern Indochina (Southeast Asia)