1st century Rome of Western, Han of Eastern and Jesus of Middle East

BC1st century (Japanese) ← → 2nd century
An important figure who appeared in the 1st century was Jesus Christ. Rather, the year he was born was originally determined to be 1st AD, so naturally he lived in the 1st century. (The 1st century is the 100 years from 1st to 100th AD). Strictly speaking, there seems to be a little lag between the year of his birth and the Christian era…
もくじ
Middle East(Israel/Palestine)
Jesus was born in what is now Israel, which at that time was ruled by the Herodian dynasty but strongly influenced by the Roman Empire, and it came under direct Roman rule during the first century. Israel was the heartland of Judaism, and because he sought to reform Judaism, he was executed by Jews who opposed him. After his death, Jesus’ teachings spread throughout the Roman Empire and the Middle East through his disciples, including Peter and Paul, and eventually developed into Christianity, a world religion.
However, the Roman Empire at the time valued its own religion (polytheism), and monotheistic Christianity was sometimes viewed as dangerous as a new religion. Therefore, it would take 300 years for Christianity to be accepted by the Roman Emperor.
The Jews, on the other hand, could no longer bear the rule of the Roman Empire and started a rebellion in 66 AD. But they were eventually suppressed and the temple in Jerusalem was destroyed.
Europe (Roman Empire)
At the time of the 1st century, the Roman Empire had just begun imperial government under Octavian (Augustus). As a result, conflicts over the imperial throne often occurred, but society as a whole was more stable than in the 1st century BC, when civil wars continued.
In 54, Emperor Nero enthroned. He is said to have imposed tyranny, blaming Christians for the great fire that broke out in Rome and oppressing them, and trying to forcefully steal wealth from the aristocrats when the financial crisis arose. Known as a tyrant. However, it is said that it was very popular with the public because it held many luxurious events (although this was the cause of its financial crisis…).
From an economic perspective, trade flourished as the Roman Empire acquired the entire Mediterranean coastline, and wealth such as wheat, wine, and gold were brought to Rome from various regions that became provinces. On the other hand, Roman-style culture was transmitted to the provinces, and the “Romanization” of the people progressed.
East Asia
In eastern Eurasia, the Han(漢) dynasty was entering a new phase. A man named Wang Mang(王莽), who was related to the imperial family, usurped the dynasty and changed the country’s name to Xin(新). Wang Mang embarked on land reform to eliminate the disparity between rich and poor, but many people opposed it, and in the end a great rebellion (Red Eyebrow Rebellion) broke out and the reform ended in failure.
After Wang Mang’s death, Liu Xiu(劉秀), a distant relative of the emperor, ascended the throne. The capital was also moved from Chang’an(长安) to Luoyang(洛阳), so the subsequent Han dynasty is called the Eastern Han(東漢). By the latter half of the 1st century, the country was generally stable, and the teachings of Confucianism, which would form the basis of later Chinese society, began to spread. On the other hand, the power of the emperor did not necessarily extend to the local areas Here, powerful families managed vast lands (manors) and accumulated power.
Japan was in the middle of the Yayoi(弥生) period, and the village in various places were gradually developing into kingdom. Among the rulers, there are those who borrow the power of Han. They sent messengers across the sea to the Eastern Han Dynasty, hoping to gain the emperor’s approval by becoming his vassals. It is said that in 57 A.D, the King of “Na”(奴) received a golden seal from the Emperor of Han.

India, Iran, and Central Asia
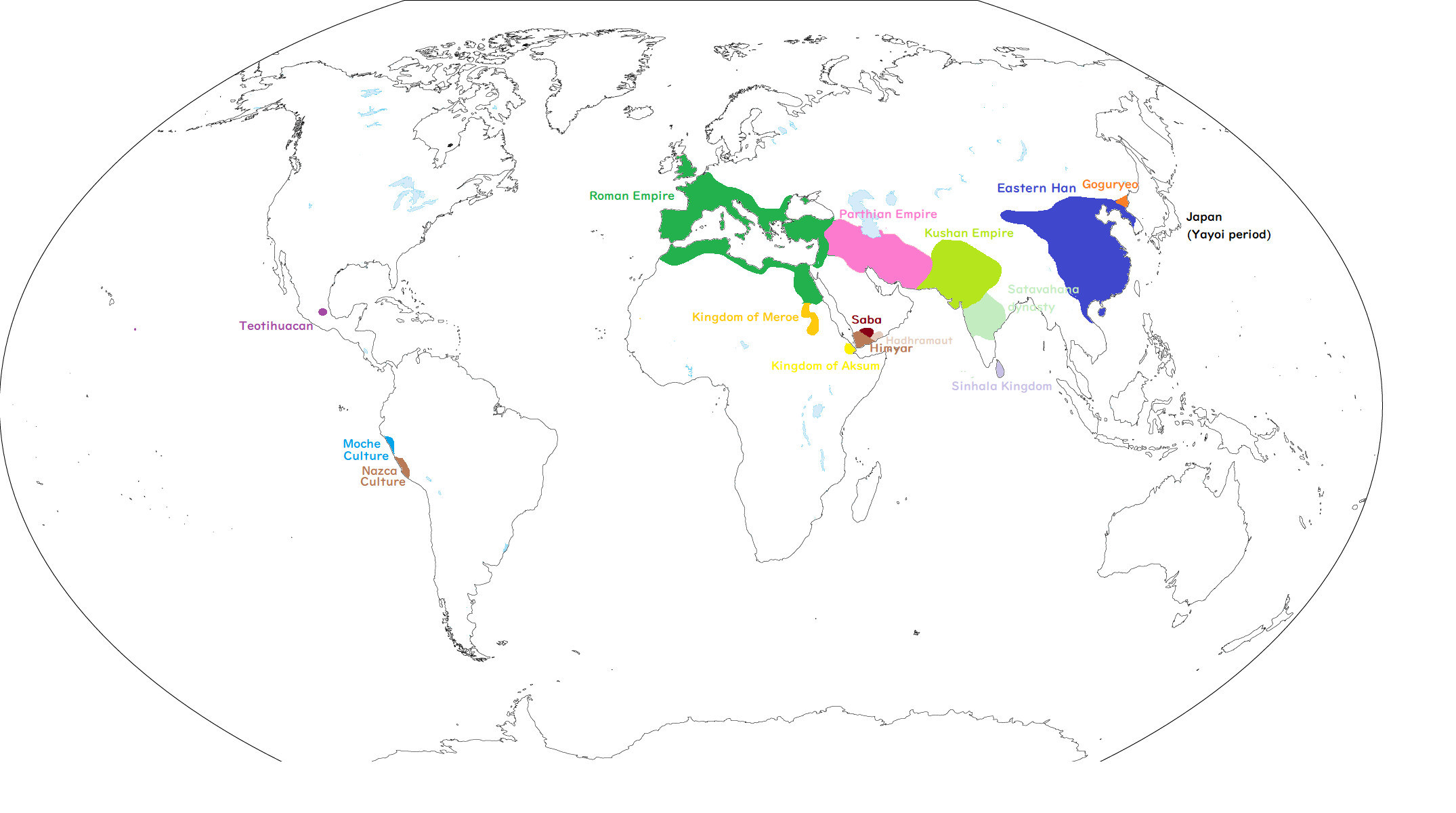
As the great empires of Rome and the Eastern Han dynasty brought stability to the western and eastern ends of Eurasia, their influence extended, directly or indirectly, to the regions between them. The Kushan dynasty (Kushan Empire), which stretched from Central Asia to northern India and lay along the so‑called Silk Road, flourished as a relay point for trade linking East and West. The Kushan royal house is thought to have been a branch of the nomadic people known as the Great Yuezhi, who migrated from China to Central Asia around the second century BCE.
In the Deccan Plateau region of southern India, the Satavahana dynasty was expanding its sphere of control. It seems to have played a major role in stimulating the movement of people via the Indian Ocean.
The Parthian kingdom, centered in what is now Iran, was also a stopover on the Silk Road. Although it was locked in a struggle for hegemony with its western neighbor, the Roman Empire, there was probably no small amount of movement of people between the two.
Meanwhile, from the east, a Chinese officer named Gan Ying(甘英) is said to have reached Parthia. His superior, Ban Chao(班超), served as the commander of the Protectorate of the Western Regions, which was responsible for maintaining security along the routes leading westward from China (the Silk Road). This shows that the Eastern Han also sought to prioritize and control this east–west trade route, and Dunhuang(敦煌), famous for the Mogao Caves(莫高窟), was one of its important relay points.
America
There are many unknowns about the Americas. In South America, the Nazca culture, known for leaving behind geoglyphs, and the Moche culture, which produced a large number of vivid earthenware, arose. In Central America, an urban civilization such as Teotihuacan also emerged.
Events
8 Wang Mang(王莽) usurped the throne and establishes Xin(新) dynasty. (China)
14 Octavian (Augustus), first emperor of Rome, passed away.
18 Red Eyebrow Rebellion (China)~25
25 Liu Xiu(劉秀) rebuilds Han(漢) and becomes Emperor Guangwu(光武帝). Eastern Han(東漢) dynasty was built. (China)
around 30 Jesus is executed on Golgotha Hill in Jerusalem. Christianity was established by the disciples. (Palestine)
40 Trưng sisters revolted against the Han. (Vietnam)
48 The nomadic Xiongnu(匈奴) were divided into north and south. (East Asia)
57 King of Na(奴) received the gold seal. (Japan)
64 Great Fire of Rome. Emperor Nero accused Christians of crimes and oppressed them.
66 First Jewish–Roman War (Palestine)
79 Mount Vesuvius erupted and the city of Pompeii was buried in ash. (Roman Empire)
80 Colosseum completed. (Roman Empire)
94 Ban Chao(班超) subjugated the Western Region. (China Xinjiang)
96 Emperor Nerva ascended the throne. Time of Five Good Emperors began.
(Year unknown)
The Kushan dynasty of Central Asia expands into northern India. (South Asia)Nazca culture and
Moche culture emerged in present-day Peru. (South America)
“Periplus of the Erythraean Sea” was written.
BC1st century (Japanese) ← → 2nd century